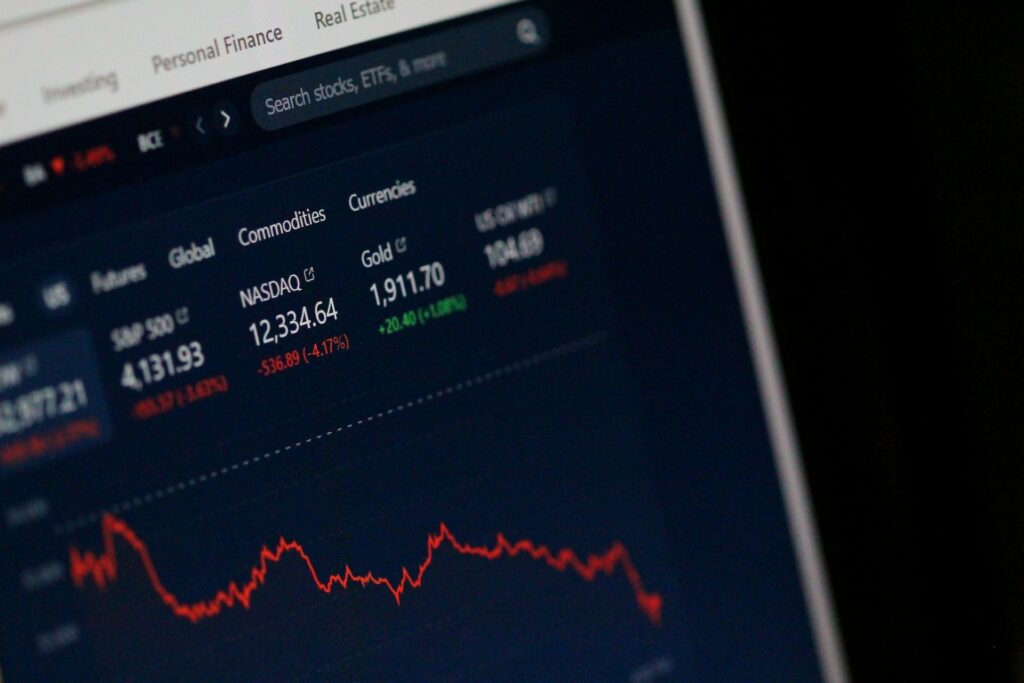
The S&P 500 index achieved an all-time high of 4,818.62 points on January 4, 2022. The Standard and Poor’s 500, or S&P 500, is a stock market index that tracks the stock performance of 500 major firms listed on U.S. stock exchanges. It is one of the most widely followed stock market indices.
Given that U.S.-listed businesses account for over 60 percent of the worldwide stock market, the movement of the index containing the 500 biggest of them reveals the true state of the global economy. And right now it’s not good at all.
On June 13, the S&P 500 closed at 3,749.91 points, reflecting a 22% decline from its peak of 4,818.62 points on January 4. Amazon, Apple, and Meta all experienced declines in their market values.
For the first time since the onset of the COVID-19 epidemic, the slump pushed equities into bear market territory — a protracted period of negative price trends. In contrast, a bull market occurs when stock values continue to rise.
As of the 12th of December, the index was at 3,990, still 17.2% below January’s level.
There have been many bear markets in the past, but this one is getting a lot of attention because of rising inflation and other factors that have some analysts worried about a recession.

What exactly is a bear market?
A bear market exists when a broad stock market index has a 20% or more loss from recent highs for at least two months.
The S&P 500 has seen 26 bear markets since 1928, according to Hartford Funds.
The opposite of a bear market is a bull market, which occurs when a broad market index such as the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average increases by 20% or more over at least two months.
According to Hartford Funds, there have been 27 bull markets since 1928, with an average duration of 991 days or 2.7 years.

How long do bear markets last?
The S&P 500 has fallen by more than 20% eleven times since 1950, according to new research from Yardeni Research.
It took 929 days for the bear market of the early 2000s to reach its lowest point. Approximately two and a half years. After the phenomenal surge of internet stocks in the late 1990s, this bear market happened.
The second-longest bear market began in 1973 and lasted for 630 days. Inflation, sluggish economic development, and the political unrest surrounding President Nixon all contributed to the economic collapse.
The bear market in 2020, caused by pandemic-related shutdowns and uncertainty, was the shortest in history. The stock market saw a 33-day decline before resuming expansion.
So, how long do bear markets typically last?
It depends on the formula employed. Since the 1920s, the average duration of an S&P 500 bear market has been 289 days, or roughly nine and a half months, according to financial analysis firm Seeking Alpha. During these bear markets, the S&P 500 dropped around 36% on average.
According to Bespoke Investment Group, the average duration of the 14 bear markets since World War II was 359 days, or over a year.
Yardeni Research says that, excluding the current bear market, the average length of a bear market is 388 days, or just over a year.
Except for the greatest and shortest bear markets of 2000 and 2020, respectively, the average duration of a bear market is over a year.

Does the recession usually follow a bear market?
Since 2000, just three bear markets have occurred outside of this one. Two of the three have outlasted the average duration of one year.
Ben Carlson of Ritholtz Wealth Management discovered, after analyzing all bear markets since World War II, that it takes one year to move from “peak to trough,” or the conclusion of a period of expansion to rock bottom.
Thus, the present bear market would reach its bottom in the beginning of 2023, one year after its top in January.
A bear market is frequently, but not always, accompanied by a recession. According to Reuters, nine of the twelve recessions after World War II were followed by bear markets.
However, since 1928 there have been 26 bear markets and just 15 recessions.
According to Bespoke Investment Group, bear markets associated with a recession are often longer (495 days against 198 days) and more severe (a 35% decline in the S&P 500 versus 28.2%).
Multiple things might contribute to a bear market. Relevant ones are the weakening economy and the escalating invasion of Ukraine and its effects on the geopolitical scene.
Parts of the economy being shut down because of the epidemic and the Federal Reserve’s decision to raise interest rates to fight inflation could be to blame.

Is now a good time to invest?
Does all of this information mentioned above indicate that now is a good time to invest? No one can predict the future with absolute certainty, especially in the near future. Historically, however, if you have a sufficiently long investing horizon, the ideal moment to invest is when the market has plummeted.
Currently, there are numerous inexpensive stocks. Even if the stock is about 50 percent lower than it was in 2021, Amazon’s business has not fundamentally altered. Neither do Apple, Microsoft, Goldman Sachs, Nvidia, or the majority of other S&P 500 corporations.
If you believed in the company six or twelve months ago, has anything other than the stock price altered since then?
“Be greedy when others are fearful, and fearful when others are greedy.” These are frequently cited Warren Buffet quotes, and there is currently a great deal of fear in the world.
Mentally, this might be a very tough moment to invest because it is impossible to predict if the market will continue to decline.
But if you can handle the ups and downs and have the stomach for it, you may be able to set up your portfolio for big long-term gains.